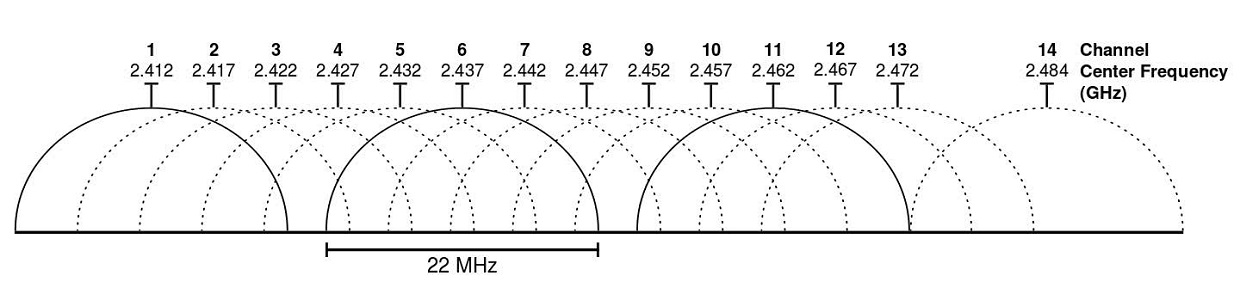
WiFi signal 4.2.1. WiFi signal system menu bar application that provides easy access to your WiFi connection details (name, speed, channel, signal strength, noise, etc.), monitors the quality of the wireless signal, and can find and recommend alternative channels network thus avoiding signal overlap and conflict between channels, which can lead to problems with connection and lost. 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channels, frequencies etc, showing overlap and which ones can be used as sets. From the diagram above, it can be seen that Wi-Fi channels 1, 6, 11, or 2, 7, 12, or 3, 8, 13 or 4, 9, 14 (if allowed) or 5, 10 (and possibly 14 if allowed) can be used together as sets.
Talking about 'good signal strength' may have become part of everyday language, but what constitutes a good Wi-Fi signal, really? Do you know what it takes to be able to use demanding services like Netflix and videoconferencing over Wi-Fi?
Signal strength is measured in dBm or decibel milliwatts, which, somewhat confusingly, is expressed only in negative values (with a minus sign in front).

Wifi Signal 4 1 2019
Widsmob montage 1 3 – stunning mosaic photographs framed. So what are the good and acceptable dBm values for wireless internet?
Here is what the Wi-Fi signal strength values mean
How to measure the received signal strength
To measure signal strength at a given location and time, you can use a Wi-Fi scanner. You can read more about this in our article How to find good Wi-Fi channels and bad neighbors.
The measurement you are looking for is RSSI, which is short for received signal strength indicator.
If you are running Mac OS X, you can also measure the received signal strength directly without installing anything: Hold down the Altkey and click the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu, and details of communication with the wireless access point will appear under the name of the active Wi-Fi network.
If you would like to map out the signal for an entire home, we recommend using a heat mapper to create a heat map of good and bad coverage zones. See also: Map your wireless network with a heat mapper.
Wifi Signal 4 1 2 X 4
Poor signal strength? Remove obstacles
Have you done your testing and concluded that the signal strength is insufficient? First of all:
Don't be tempted to try to amplify the transmit strength from your router / access point. You may sabotage both yourself and your neighbors in the process, and you risk breaking the law along the way. Read more about this in Don't. Boost. Your Wi-Fi Signal.
Of course, the performance and capacity of the wireless network depends on more than the signal emitted from the access point, but the most important thing you can do for the signal is:
- Move the router or other access point high up and in front of any obstacles. Preferably high up on the wall.
- Place your devices and access points with as much of a clear line of sight between them as possible.
Get further advice on what you can do yourself to improve your home Wi-Fi in: Better Wi-Fi at Home: 18 Free Tips.
Article by Jan Pedro Tumusok and Jorunn D. Newth
Wifi Signal 4 1 2019
Widsmob montage 1 3 – stunning mosaic photographs framed. So what are the good and acceptable dBm values for wireless internet?
Here is what the Wi-Fi signal strength values mean
How to measure the received signal strength
To measure signal strength at a given location and time, you can use a Wi-Fi scanner. You can read more about this in our article How to find good Wi-Fi channels and bad neighbors.
The measurement you are looking for is RSSI, which is short for received signal strength indicator.
If you are running Mac OS X, you can also measure the received signal strength directly without installing anything: Hold down the Altkey and click the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu, and details of communication with the wireless access point will appear under the name of the active Wi-Fi network.
If you would like to map out the signal for an entire home, we recommend using a heat mapper to create a heat map of good and bad coverage zones. See also: Map your wireless network with a heat mapper.
Wifi Signal 4 1 2 X 4
Poor signal strength? Remove obstacles
Have you done your testing and concluded that the signal strength is insufficient? First of all:
Don't be tempted to try to amplify the transmit strength from your router / access point. You may sabotage both yourself and your neighbors in the process, and you risk breaking the law along the way. Read more about this in Don't. Boost. Your Wi-Fi Signal.
Of course, the performance and capacity of the wireless network depends on more than the signal emitted from the access point, but the most important thing you can do for the signal is:
- Move the router or other access point high up and in front of any obstacles. Preferably high up on the wall.
- Place your devices and access points with as much of a clear line of sight between them as possible.
Get further advice on what you can do yourself to improve your home Wi-Fi in: Better Wi-Fi at Home: 18 Free Tips.
Article by Jan Pedro Tumusok and Jorunn D. Newth
| Signal Strength | Required for | |
| -30 dBm | Max achievable signal strength. The client can only be a few feet from the AP to achieve this. Not typical or desirable in the real world. | N/A |
| -67 dBm | Minimum signal strength for applications that require very reliable, timely packet delivery. | VoIP/VoWiFi, streaming video |
| -70 dBm | Minimum signal strength for reliable packet delivery. | Email, web |
| -80 dBm | Minimum signal strength for basic connectivity. Packet delivery may be unreliable. | N/A |
| -90 dBm | Approaching or drowning in the noise floor. Any functionality is highly unlikely. | N/A |
And what about SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio)
SNR is not actually a ratio but the difference in decibels between the received signal and the background noise level (noise floor). For example, if a radio (client device) receives a signal of -75 dBm and the noise floor is measured at -90 dBm, the SNR is 15 dB. Data corruption and therefore re-transmissions will occur if the received signal is too close to the noise floor. In 802.11 networks, re-transmissions adversely affect throughput and latency.
Wifi Signal 4 1 20
Red giant trapcode particular 3 1 1 download free. How does RSSI (dBm) relate to signal quality (percent)?
Depending on your OS and application, WiFi signal strength is represented either as quality in percentage, or an RSSI value in dBm, i.e. -70db. RSSI is usually expressed in decibels from 0 (zero) to -120db and the closer it is to zero, the stronger the signal is. RSSI level less than -80db may not be usable, depending on noise.
While there is no simple precise solution that is used universally, we will try to explain the approximate correlation between signal (RSSI) and quality (percentage).
Generally,
db >= -50 db = 100% quality
db <= -100 db = 0% quality
For RSSI signal between -50db and -100db,
quality ~= 2* (db + 100)
RSSI ~= (percentage / 2) - 100
For example:
High quality: 90% ~= -55db
Medium quality: 50% ~= -75db
Low quality: 30% ~= -85db
Unusable quality: 8% ~= -96dbDepending on your OS and application, WiFi signal strength is represented either as quality in percentage, or an RSSI value in dBm, i.e. -70db. RSSI is usually expressed in decibels from 0 (zero) to -120db and the closer it is to zero, the stronger the signal is. RSSI level less than -80db may not be usable, depending on noise.
While there is no simple precise solution that is used universally, we will try to explain the approximate correlation between signal (RSSI) and quality (percentage).
Generally,
db >= -50 db = 100% quality
db <= -100 db = 0% quality
For RSSI signal between -50db and -100db,
quality ~= 2* (db + 100)
RSSI ~= (percentage / 2) - 100
For example:
High quality: 90% ~= -55db
Medium quality: 50% ~= -75db
Low quality: 30% ~= -85db
Unusable quality: 8% ~= -96db

